Categories
In this article
- Default Microsoft 365 Retention
- Retention Policy and Retention Labels
- eDiscovery Hold
- Versioning
- Third-party Backup Solution
SharePoint data retention at a glance
- Deleted files are moved to the recycle bin and retained for 93 days before permanent deletion.
- Advanced licenses offer additional retention policies and eDiscovery capabilities but lack automated recovery features.
A Complete Guide to Microsoft SharePoint Data Retention
29 Nov 2024
8 min read
SharePoint is a web-based collaboration and document management solution with over 190 million users across 200,000 organizations, including 78% of Fortune 500 companies. SharePoint primarily serves as a data storage location for other Microsoft 365 apps and a means to share information across an organization
Businesses' widespread adoption of SharePoint also means that there is an increased risk of data loss for various reasons. Since Microsoft is not responsible for backing up your data, IT administrators are responsible for retaining SharePoint Online data so that business data is always available.
What are the apps that use SharePoint as their data storage location?
Learn more about the differences between OneDrive and SharePoint.
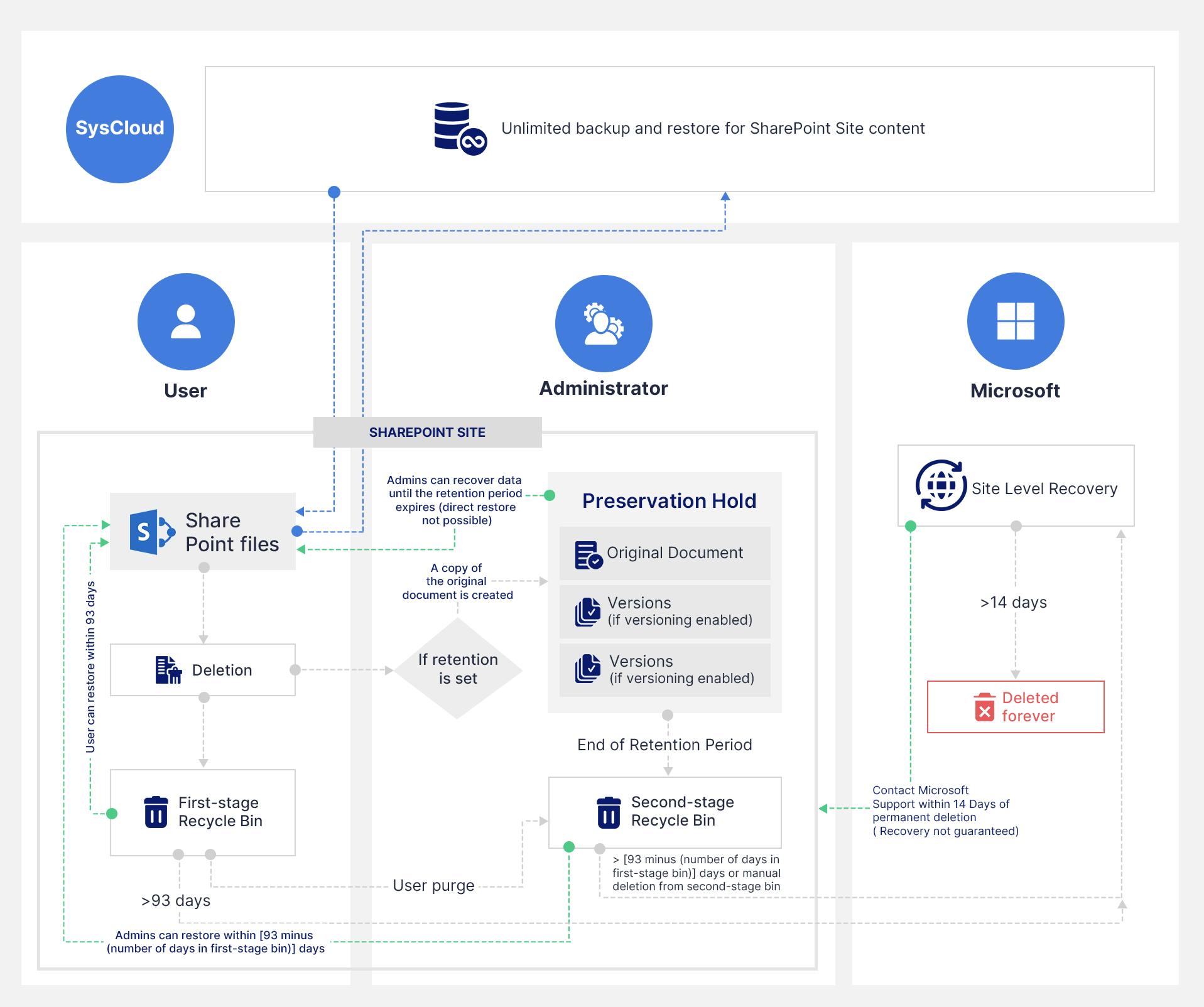
Default Microsoft 365 retention in SharePoint
Note: The standard retention period (93 days) begins when something is first deleted and does not change if the deleted item moves from the first-stage to second-stage Recycle Bins.
Methods to retain SharePoint Online data
Retention policies and retention labels
A retention policy is used to assign retention settings to content at a site or mailbox level whereas a retention label is used to assign retention settings at an item level (to a particular document, file, or email).
Admins can manage retention policies and labels via the Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
To know when to use retention policies and labels, how to create them, and how they differ from each other, read our in-depth article: Microsoft 365 Retention Policy and Retention Label: A Complete Guide
Records management
For more information on records management, refer to Microsoft's documentation on Records Management.
Principles of retention
- Retention always takes precedence over permanent deletion.
- The longest retention period wins.
- Delete actions from a retention label take precedence over delete actions from a retention policy.
- The shortest deletion period wins.
For more detailed information on these principles, refer to Microsoft's documentation on Retention Policies and Retention Labels.
Preservation lock for retention labels and policies
Note: A Preservation Lock is irreversible and should be used cautiously.
- No one can disable or delete it
- Locations can be added but not removed
- You can extend the retention period but not decrease it
- No one can disable or delete it
- Locations can be added but not removed
- Labels can be added but not removed
For guidance on how to lock a retention policy, refer to Microsoft's documentation on Preservation Lock.
eDiscovery holds
To learn how to create an eDiscovery hold, refer to this article A Primer to Microsoft 365 eDiscovery Solutions
Versioning
Note: Be aware that SharePoint Online has a default limit of 500 versions for documents (which can be adjusted). Retention policies can preserve versions in the Preservation Hold library, impacting storage.
How to enable versioning in SharePoint?
Step 1: Navigate to the library you want to enable versioning
Step 2: Click on the Settings icon and select Library settings -> More library settings

Step 3: In the window that opens, click on Versioning settings.

Step 4: Configure the settings and click OK.

Third-party cloud backup solutions
While the native settings offered by Microsoft are helpful in retaining your data for legal compliance, they do not serve as a backup solution. Microsoft is not responsible for backing up your data and they recommend using third-party apps for backup. Here is what Microsoft says in their Services Agreement (Section 6.b).
We strive to keep the Services up and running; however, all online services suffer occasional disruptions and outages, and Microsoft is not liable for any disruption or loss you may suffer as a result. In the event of an outage, you may not be able to retrieve Your Content or Data that you’ve stored. We recommend that you regularly backup Your Content and Data that you store on the Services or store using Third-Party Apps and Services.
Why should you have a third-party cloud backup solution?
Limitations of Native Retention Settings: The native retention settings offered by Microsoft do not serve as an effective data backup and recovery option. Having a third-party cloud backup solution will shield your data during data loss incidents.
- Granular Restoration: Third-party cloud backup tools such as SysCloud help you easily restore specific or all files in just a few clicks.
- Save License Costs: Having a backup allows you to retain safe copies of organizational data even after employee exits and account deletions, thus saving license costs.
- Protection Against Ransomware and Other Cyberattacks: Third-party backup tools can secure your data during ransomware attacks by automatically identifying a safe backup snapshot to restore the affected file(s).
How SysCloud offers advanced data retention and recovery options for SharePoint Online
- Restore specific or all sites back to the user account in just a few clicks without the trouble of importing and exporting
- Directly restore data back to its previous location with all sharing permissions and folder structure still intact
- Restore data to another user’s account
- Permit employees to restore their files to facilitate faster recovery.
- Receive regular reports on the status of your backup, restore, and export reports.
- Define retention rules for an unlimited period.
- Locate and recover SharePoint data within the backup archives using advanced search options.
Check our comparison table for a detailed look at how SysCloud measures up against SharePoint Online's native retention features: SysCloud vs. Microsoft 365 Native Retention
Recommended content
21 Dec 2021
3 min read
2 May 2024
8 min read
21 Jan 2022
12 min read
10 Sep 2024
8 min read
Get actionable SaaS administration insights
We don’t spam. Unsubscribe anytime.
In this article
- Default Microsoft 365 Retention
- Retention Policy and Retention Labels
- eDiscovery Hold
- Versioning
- Third-party Backup Solution

