Categories
In this article
- Introduction
- Why data retention?
- Where is Google Sites data stored?
- What happens when Google Sites data is deleted?
- Native retention settings using Vault
- Retention rules
- eDiscovery holds to retain Sites data
- Are Google Vault retention and eDiscovery ideal data backup solutions?
A Guide to Google Sites Retention
29 Nov 2021
12 min read
Ragavarshini
Google Sites retention at a glance
- Deleted sites, pages, or content may be lost forever if not recovered within 30 days of deletion.
- Google Vault offers limited retention rules for Google Sites, applicable only to specific licenses, and lacks automation.
Read more
1. Introduction
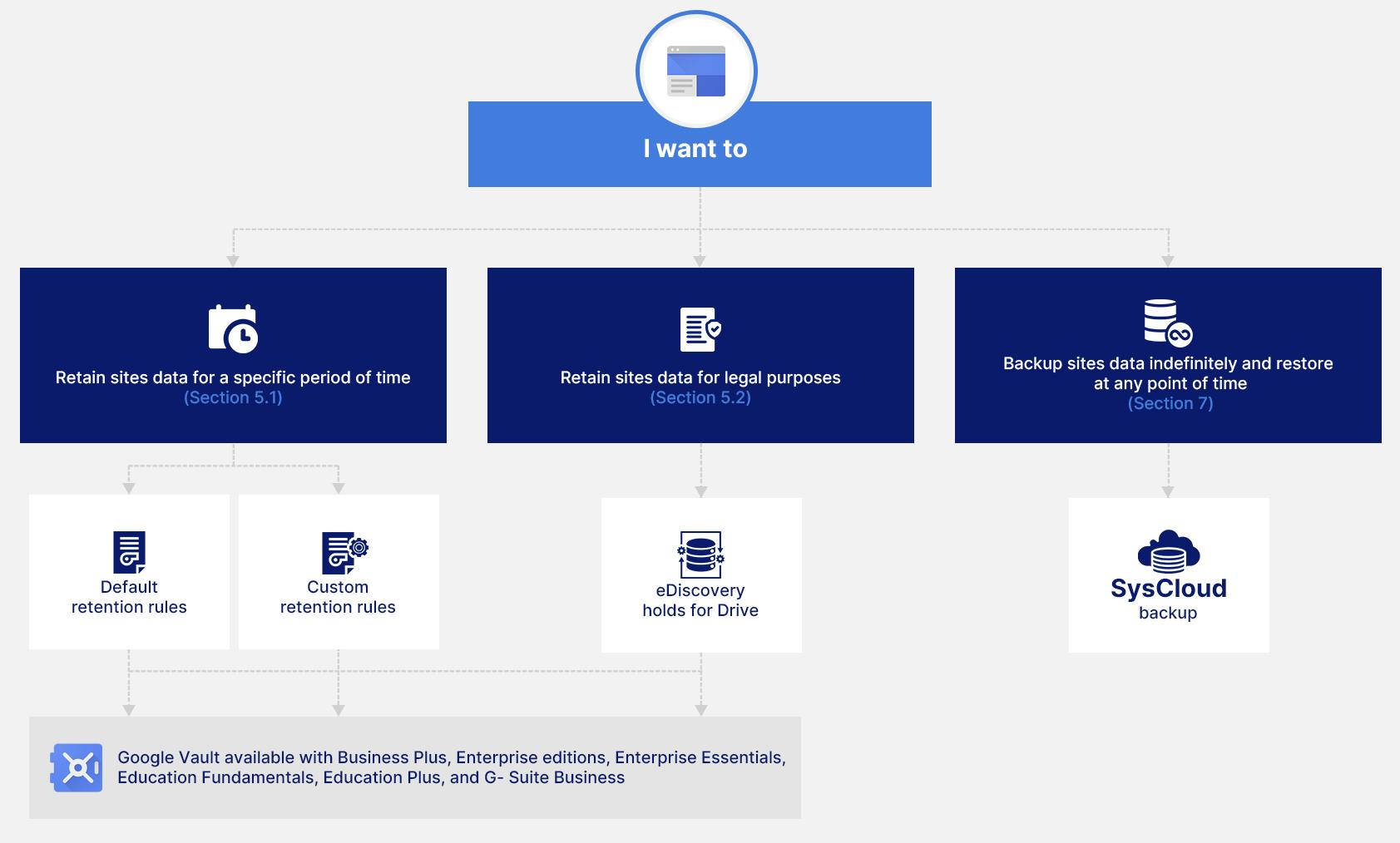
2. Why data retention?
Data retrieval in case of accidental deletion
When a Google site is hard deleted, it is lost forever unless retention policies are in place. Using retention helps you manage data deletion and recovery efficiently, thus increasing business productivity.Storage management
Google Workspace storage is shared between Gmail, Drive, Sites, Photos and Docs. The amount of free storage for each user depends on the type of account opted. Employees should not be forced to delete data once the storage limits are reached and at the same time, remove data that are no longer needed. Implementing retention policies saves storage costs by only retaining essential data.
Statutory regulation & compliance
Regulated industries such as healthcare, legal, and finance are required to retain certain data for a longer duration. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act, for example, specifies the standards for financial document record-keeping and having controls in place to retain data.
3. Where is Google Sites data stored?
Note:
1. Google announced that from January 1, 2023, classic Sites will no longer be viewable. To continue to view the sites, you must convert and publish them to the new Google Sites experience before January 1, 2023.
4. What happens when Google Sites data is deleted?
To know how a Google Workspace Administrator can recover permanently deleted files from Google Admin Console, click here.
Note: If the site is shared, collaborators can still make a copy of it before it is permanently deleted.
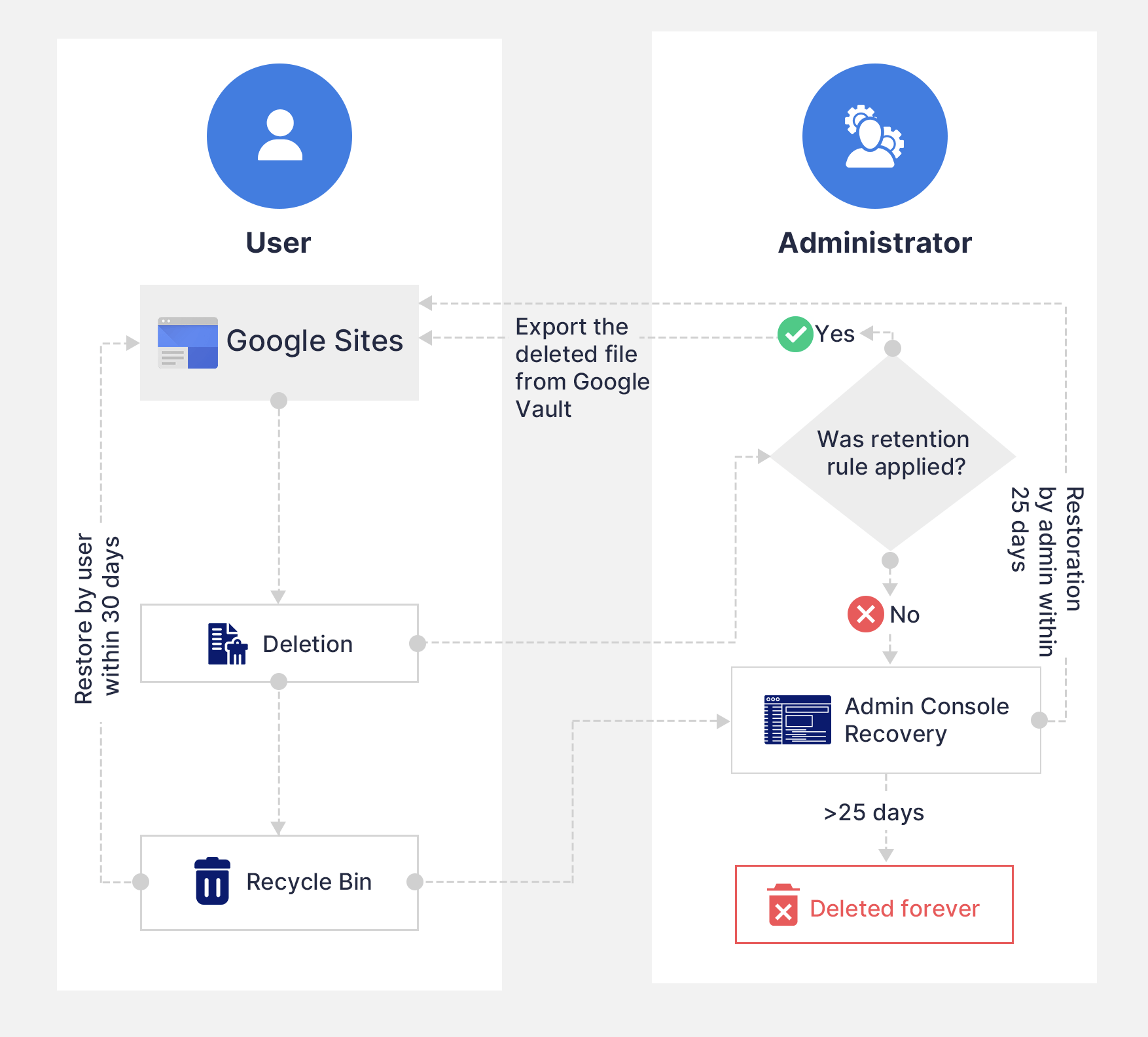
4.1. Limitations of default Sites retention
Sites retained using the default retention is counted towards your Google Workspace storage quota, and you will need to purchase additional storage if you exceed the limit. The amount of free storage for each user depends on the type of account opted.
- As seen in the illustration, Sites data is permanently deleted after the 30-55 days timeframe.
5. Native retention settings using Vault
To learn in detail about Google Vault, Vault retention rules, holds, and license requirements, read our in-depth article on Google Vault Fundamentals.
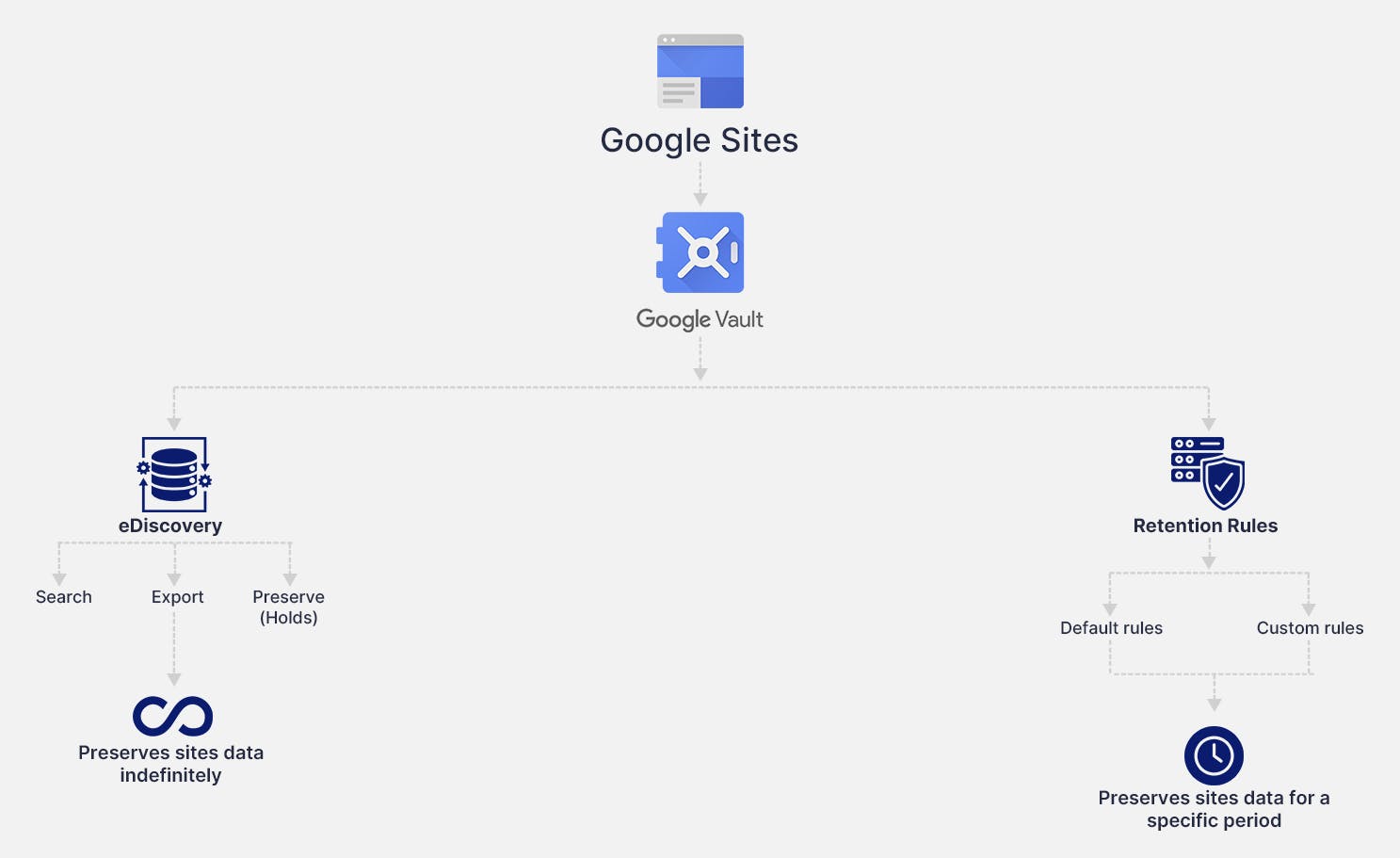
5.1. Retention rules
To manage Site retention, you can set Sites-specific retention rules. By default, Site-retention rules are turned on. If you do not have any rules created for Sites, data will be retained or purged according to rules set in Google Drive. To know more about how to create rules for Google Drive, click here.
Default retention rules
Note: Irrespective of how Sites are retained, Drive holds always apply to Sites.
How to create default retention rule for Sites?
Step 1: Sign in to Google Vault.
Step 2: Click ‘Retention’, and the select ‘Sites’.
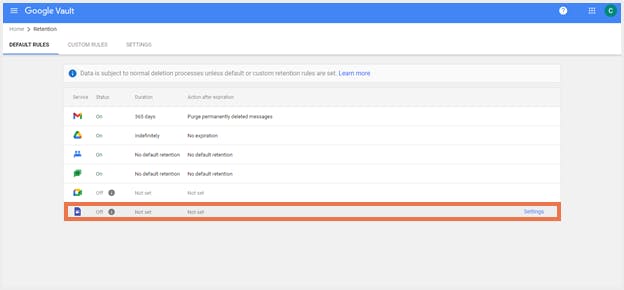
Step 3: Under ‘Duration’, choose how long files need to be retained.
a. To permanently retain files, select ‘Indefinitely’.b. To discard files after a set time, select ‘Retention Period’, plug in the number of days it needs to be retained, and the start of the reference period
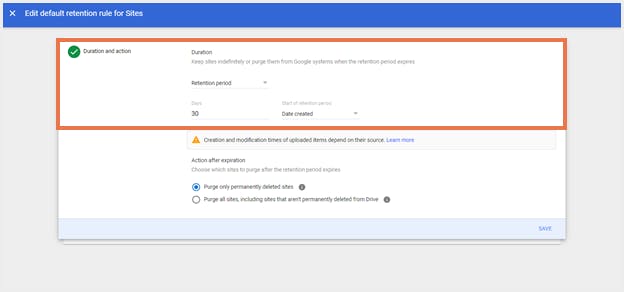
Step 4: If a duration has been set, choose what to do with sites after the retention period ends:
a. To purge only sites that users deleted, select ‘Purge only permanently deleted sites.’b. To purge all sites, choose the second option. This rule can purge both deleted sites and sites in Drive.
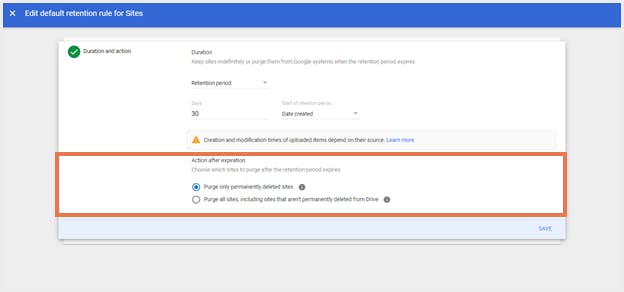
Step 5: Click ‘Save’.
Note: Since Sites-specific retention is turned on by default, make sure you double-check the rule before clicking ‘Save’. Google Vault immediately purges sites that exceed the retention duration.
Custom retention rules
Note:
How to create custom retention rules for Sites?
Step 1: Sign in to Google Vault.
Step 2: Click ‘Retention’, select ‘Custom Rules’, and then click ‘Create’.
Step 3: Select ‘Sites’ under Service, and then click Continue.
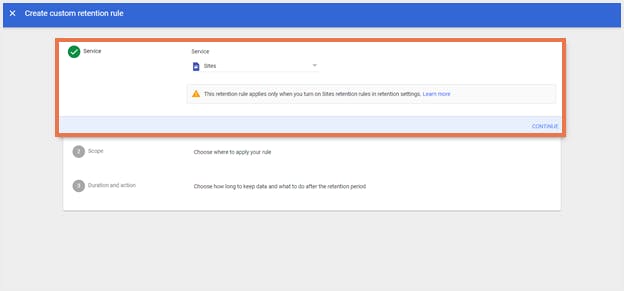
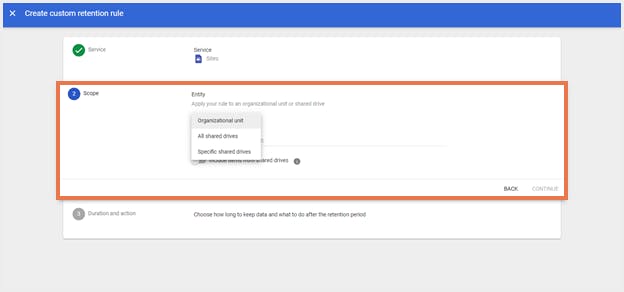
Step 4: Under ‘Scope’, choose an entity, and click ‘Continue’.
a. Select ‘Organizational unit’ to apply the rule to a specific organizational unit and choose the unit. If you want to apply the rule to shared drives that accounts in the selected organizational unit are members of, enable ‘Include results from shared drives’.b. Select ‘All shared drives’ to apply the rule to all shared drives in the organization.c. Select ‘Specific shared drive’ to apply the rule to a shared drive shared with a specific account and choose the corresponding account(s).
Step 5: Under ‘Duration’, choose how long files need to be retained.
a. To permanently retain files, select ‘Indefinitely’.b. To discard files after a set time, select ‘Retention Period’, plug in the number of days it needs to be retained, and the start of the reference period.
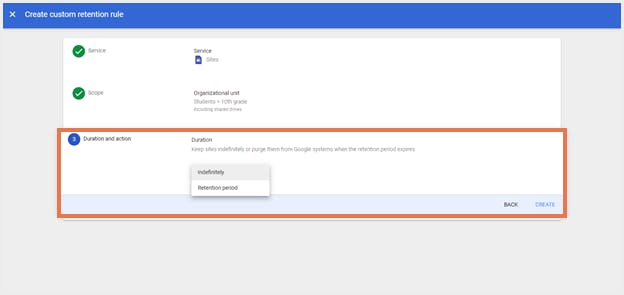
Step 6: If a duration has been set, choose what to do with sites after the retention period ends:
a. To purge only sites that users deleted, select ‘Purge only permanently deleted sites.’b. To purge all sites, choose the second option. This rule can purge both deleted sites and sites in Drive.Step 7: Click ‘Create’.
Retain Sites according to Drive rules
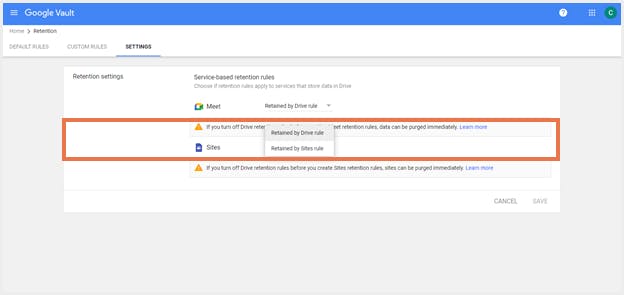
Step 1: Sign in to Google Vault.
Step 2: Click ‘Retention’ and navigate to the ‘Settings’ tab.
Step 3: Next to Sites, select ‘Retained by Sites rule’ or ‘Retained by Drive rule’.
Step 4: Click ‘Save’.
What Google Sites data can be retained using Google Vault?
| Items within scope of retention | Items outside scope of retention |
|---|---|
|
|
5.2. eDiscovery holds to retain Sites data
Note: No matter how Sites are retained, Drive holds always apply to Sites.
To learn more about eDiscovery holds in Google Drive, check out this article.
6. Are Google Vault retention and eDiscovery ideal data backup solutions?
User deletions: If a user is deleted from your Google Workspace account, all the associated Sites data also gets purged even if it was on hold or covered by a retention policy. This is because Google Vault does not make a second copy of the Sites data, it simply keeps it on hold to prevent deletions.
Absence of restore feature: Sites data that is retained through Google Vault can only be exported and not directly restored back into your account.
Google outages: Unexpected Google outages can result in data being inaccessible for hours. This can hugely impact business productivity.
Cyber threats: If your Google Sites data falls prey to cyber threats such as ransomware, the data retained and held in Google Vault also gets affected.
Third-party cloud backup solutions like SysCloud are a one stop solution to your data backup and restore problems.
Note: Due to API unavailability for New Google Sites, SysCloud backs up Classic Google Sites only.
Recommended content
5 Jan 2022
7 min read
6 Dec 2021
15 min read
Get actionable SaaS administration insights
We don’t spam. Unsubscribe anytime.
In this article
- Introduction
- Why data retention?
- Where is Google Sites data stored?
- What happens when Google Sites data is deleted?
- Native retention settings using Vault
- Retention rules
- eDiscovery holds to retain Sites data
- Are Google Vault retention and eDiscovery ideal data backup solutions?

